Knee injuries can be debilitating and require specialized care for effective recovery. Whether it’s due to sports, accidents, or overuse, knee injuries can impact mobility and overall quality of life. In this article, we will explore the various rehabilitation and therapy techniques, surgical interventions, and preventive measures for knee injuries, providing valuable insights for both patients and healthcare professionals.
Key Takeaways
- Proper rehabilitation techniques are crucial for restoring knee function and mobility.
- Preventive measures such as proper warm-up and use of protective gear can help reduce the risk of knee injuries.
- Physical therapy plays a vital role in the recovery process for knee injuries, promoting strength and flexibility.
- Surgical interventions like arthroscopic surgery and knee replacement can provide effective solutions for severe knee injuries.
- Balance and proprioception exercises are essential for improving stability and reducing the risk of re-injury.
Understanding Knee Injuries
Anatomy of the Knee
The knee joint is a complex structure that plays a crucial role in supporting our body weight and facilitating movement. It consists of several components, including the femur, tibia, and patella, which work together to provide stability and flexibility. Understanding the anatomy of the knee is essential for comprehending the impact of injuries and the subsequent rehabilitation process.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Femur | Thigh bone |
| Tibia | Shin bone |
| Patella | Knee cap |
Types of Knee Injuries
Knee injuries can vary in severity and complexity, often requiring specialized treatment and rehabilitation. Understanding the specific nature of each injury is crucial for developing an effective recovery plan. For instance, a meniscus tear may necessitate different rehabilitation techniques than a ligament injury. It is important to tailor our approach to the unique characteristics of each injury, ensuring comprehensive care and optimal outcomes.
Causes of Knee Injuries
Knee injuries can be caused by a variety of factors, including overuse and repetitive stress on the knee joint. Other common causes include sudden trauma from falls or sports-related accidents. It’s important to understand the specific cause of the injury in order to develop an effective rehabilitation plan. In some cases, the cause of the injury may also influence the choice of surgical intervention. For example, a traumatic injury may require a different approach than an injury caused by overuse. Understanding the underlying cause is crucial for tailoring the rehabilitation process to the individual’s needs.
Rehabilitation Techniques
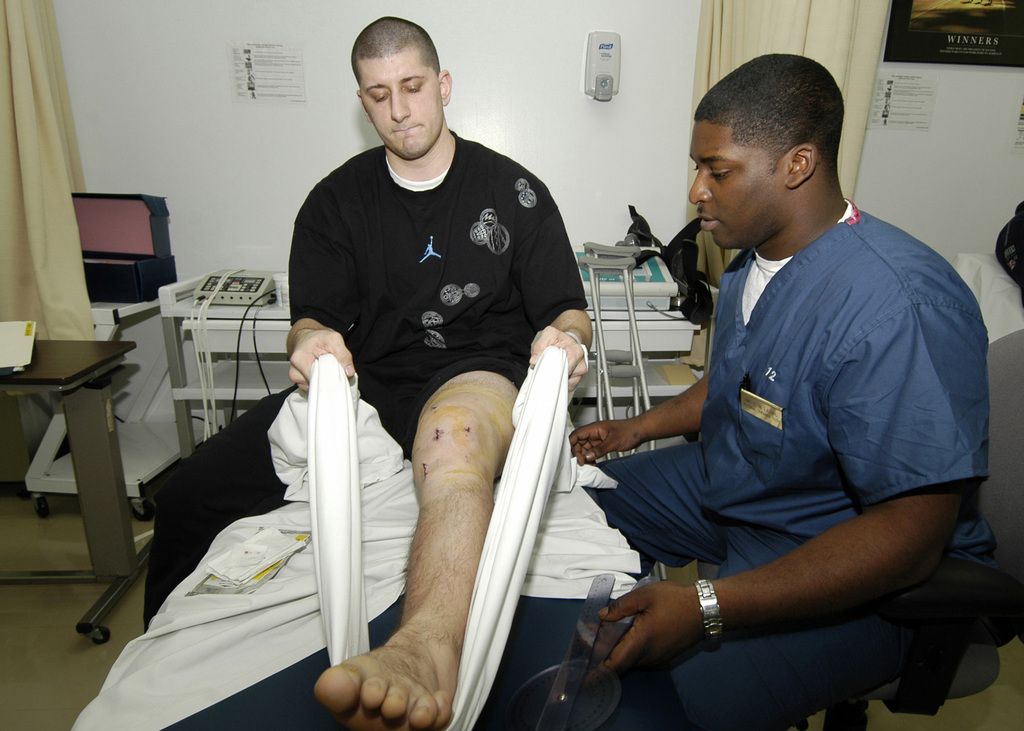
Physical Therapy
In our approach to rehabilitation, we emphasize the importance of physical therapy as a cornerstone for recovery from knee injuries. It’s a misconception that physical therapy is reserved only for athletes or those recovering from surgery. In fact, it benefits individuals across all ages and activity levels by alleviating pain and encouraging healing.
Our physical therapy programs are tailored to meet the specific needs of each patient. They often include a combination of manual therapy, therapeutic exercises, and modalities such as heat or ice application, and electrical stimulation. Here’s a brief overview of what a typical program might involve:
- Assessment of the patient’s current functional abilities
- Development of a personalized treatment plan
- Manual therapy techniques to improve joint mobility
- Exercises to restore strength and range of motion
- Education on proper body mechanics and knee care
Tip: Consistency in attending physical therapy sessions and adhering to prescribed exercises at home is key to a successful recovery.
By engaging in a structured physical therapy program, patients can expect not only to manage their symptoms but also to regain a level of function that allows for a return to daily activities and, where possible, sports.
Strength and Flexibility Training
After completing the Strength and Flexibility Training, it is important for us to focus on maintaining a balance between strength and flexibility. This balance is crucial for preventing future injuries and ensuring optimal knee function. One way to achieve this balance is through a combination of resistance training and stretching exercises.
Additionally, a structured approach to tracking progress can be beneficial. Here’s a table to track the progress of strength and flexibility training:
| Week | Strength Training Progress | Flexibility Training Progress |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Moderate | Good |
| 2 | Good | Very Good |
| 3 | Very Good | Excellent |
In addition to the table, it’s important to note that consistency and gradual progression are key to achieving the desired results. By gradually increasing the intensity and duration of the exercises, we can effectively improve both strength and flexibility.
Remember to consult with a qualified physical therapist or healthcare professional to customize the training program according to individual needs and limitations.
Balance and Proprioception Exercises
Following the strengthening and flexibility routines, we incorporate balance and proprioception exercises into our rehabilitation program. These exercises are crucial as they help in restoring the knee’s ability to sense its position in space, which is vital for preventing re-injury. We focus on exercises that challenge the body’s balance and stability, gradually increasing the difficulty as the patient’s condition improves.
One effective method we use is the single-leg stance, which can be performed with or without support. As patients progress, we introduce dynamic movements such as the single-leg squat or use of a balance board. It’s important to note that these exercises not only aid in knee recovery but also enhance overall body coordination and agility.
Remember: Consistency in performing balance and proprioception exercises is key to a successful knee injury rehabilitation. It’s not about the intensity but rather the regularity and proper execution of the exercises that contribute to a steady recovery.
Here is a simple progression of exercises we recommend:
- Single-leg stance (with support)
- Single-leg stance (without support)
- Single-leg squat
- Balance board exercises
By adhering to this progression, patients can expect a gradual return to their pre-injury levels of stability and confidence in their knee function.
Surgical Interventions
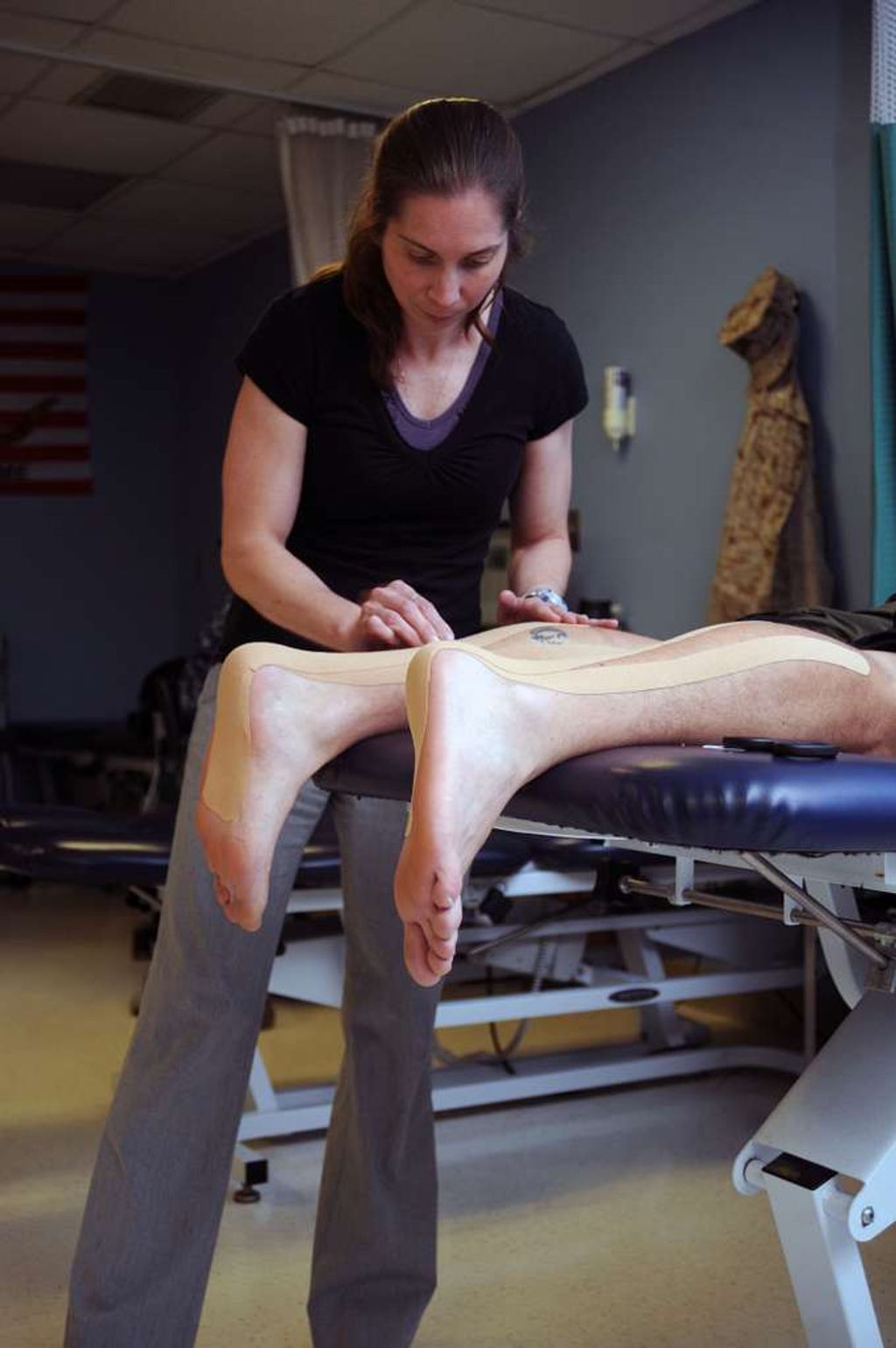
Arthroscopic Surgery
After undergoing arthroscopic surgery, rehabilitation is crucial for a successful recovery. Our rehabilitation program focuses on pain management, restoring range of motion, and strengthening the muscles around the knee. It involves a combination of physical therapy, strength training, and flexibility exercises. Additionally, patients are encouraged to engage in low-impact activities such as swimming and cycling to maintain cardiovascular fitness without putting excessive stress on the knee.
For a structured approach to rehabilitation milestones, refer to the following table:
| Milestone | Timeline |
|---|---|
| Start physical therapy | 1-2 weeks post-op |
| Full range of motion | 4-6 weeks post-op |
| Return to light sports | 3-4 months post-op |
It’s important to note that each patient’s recovery timeline may vary, and progress should be monitored closely by a qualified healthcare professional. Our team is dedicated to providing personalized care and support throughout the rehabilitation process.
Tip: Gradually increase the intensity of exercises and activities as advised by your physical therapist to avoid overexertion and minimize the risk of re-injury.
Knee Replacement Surgery
After undergoing knee replacement surgery, rehabilitation is crucial for a successful recovery. Our team focuses on a comprehensive approach to rehabilitation, including physical therapy, strength and flexibility training, and balance and proprioception exercises. These techniques are designed to improve mobility, reduce pain, and enhance overall function. Additionally, we emphasize the importance of a gradual return to daily activities and provide personalized guidance to support each patient’s unique needs.
Furthermore, our rehabilitation program incorporates a combination of passive and active range of motion exercises to optimize joint mobility and prevent stiffness. Patients are encouraged to engage in low-impact activities such as swimming or cycling to maintain cardiovascular fitness without placing excessive stress on the knee. Our goal is to promote a smooth transition from post-surgery recovery to a return to an active and fulfilling lifestyle.
For a more detailed overview of the rehabilitation process, refer to the following table:
| Rehabilitation Phase | Duration (weeks) | Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Immediate Post-Surgery | 1-2 | Pain management, gentle movement |
| Early Rehabilitation | 3-6 | Strengthening, range of motion exercises |
| Advanced Rehabilitation | 7-12 | Functional training, gradual activity |
In addition to these structured phases, it is essential for patients to adhere to the guidance provided by our rehabilitation team. This includes maintaining a positive mindset, following prescribed exercises, and communicating any concerns or progress to our healthcare professionals. Our team is dedicated to supporting each patient throughout the rehabilitation journey, ensuring a successful recovery and a return to an active, pain-free lifestyle.
Recovery and Rehabilitation After Surgery
Following knee surgery, we enter a critical phase where our focus shifts to recovery and rehabilitation. It’s essential to adhere to a structured rehabilitation plan to ensure the best possible outcome. This plan typically includes a combination of supervised physical therapy sessions and exercises to be performed at home.
Consistency is key in the rehabilitation process. We recommend daily exercises to improve knee strength and flexibility. It’s important to track progress over time, which can be facilitated by apps like Curovate, which offers features such as knee range measurement and virtual physiotherapy.
Here’s a simple outline of a post-surgery rehabilitation timeline:
- Week 1-2: Gentle range-of-motion exercises
- Week 3-4: Gradual weight-bearing exercises
- Week 5-6: Strength and flexibility training
- Week 7+: Return to normal activity levels, as advised by a healthcare professional
Tip: Always consult with your therapist before advancing to the next stage of exercises to prevent any setbacks in your recovery.
Preventive Measures
Injury Prevention Strategies
Injury prevention is a crucial aspect of maintaining knee health. It involves adopting appropriate warm-up and cool-down routines, using protective gear, and implementing strategies to reduce the risk of knee injuries. Proper warm-up and cool-down routines help prepare the muscles and joints for physical activity and aid in preventing strains and injuries. Using protective gear, such as knee braces or pads, can provide an extra layer of protection during physical activities. Additionally, implementing strategies for reducing the risk of knee injuries, such as avoiding sudden changes in intensity or duration of physical activities, can significantly contribute to maintaining knee health. It’s important to be mindful of these preventive measures to safeguard the well-being of our knees.
Proper Warm-Up and Cool-Down
We understand the importance of preparing the body for physical activity and allowing it to recover afterward. A proper warm-up gradually revs up the cardiovascular system by raising the body temperature and increasing blood flow to the muscles. Cooling down after exercise is just as crucial for reducing the heart rate and stretching the muscles to prevent stiffness and soreness.
Warm-up routines should include dynamic stretches that mimic the movements of the activity you’re about to perform. Here’s a simple sequence we might follow before a run:
- Light jogging or brisk walking for 5-10 minutes
- Gentle dynamic stretches (leg swings, arm circles)
- Gradual build-up of running speed
For cool-down, a similar approach helps in returning the body to a state of rest:
- Slow down the pace of the activity gradually
- Static stretches focusing on major muscle groups
- Deep breathing exercises to lower the heart rate
Remember, the goal of warm-up and cool-down is to bridge the gap between rest and exercise, reducing the risk of injury and improving overall performance.
Use of Protective Gear
When engaging in physical activities, protective gear plays a crucial role in minimizing the risk of knee injuries. It is important to ensure that the gear fits properly and provides adequate support. Additionally, wearing knee braces can help stabilize the knee joint and reduce the impact of sudden movements. Proper selection and use of protective gear can significantly contribute to injury prevention and overall safety during physical activities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the effective rehabilitation and therapy for knee injuries play a crucial role in the recovery and restoration of knee function. Through a combination of physical therapy, exercise, and patient education, individuals can achieve improved mobility and reduced pain. It is imperative for healthcare professionals to tailor treatment plans to the specific needs of each patient, considering factors such as age, severity of injury, and overall health. Further research and advancements in rehabilitation techniques are essential to continually enhance the outcomes for individuals with knee injuries.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common types of knee injuries?
Common types of knee injuries include ACL tear, meniscus tear, patellar tendonitis, and knee sprains.
How long does it take to recover from knee surgery?
Recovery time from knee surgery varies depending on the type of surgery and individual healing capacity. It can range from a few weeks to several months.
What are some effective physical therapy exercises for knee rehabilitation?
Effective physical therapy exercises for knee rehabilitation include leg lifts, knee extensions, hamstring curls, and quadriceps sets.
Are there any specific exercises to improve balance and proprioception after a knee injury?
Yes, exercises such as single-leg stance, balance board exercises, and agility drills can help improve balance and proprioception after a knee injury.
What are the best preventive measures to avoid knee injuries during physical activities?
The best preventive measures include proper warm-up and cool-down routines, use of protective gear such as knee braces, and adherence to injury prevention strategies such as avoiding overtraining and maintaining proper form during exercises.
Can knee injuries be prevented through strength and flexibility training?
Yes, strength and flexibility training can help prevent knee injuries by improving muscle strength, joint stability, and overall flexibility, reducing the risk of injury.
Leave a Reply